.png)
ASIO‑Medical Platform
Multi-interface medical system with RBAC, analytics, billing, and AI-assisted diagnostics.
.png)
Multi-interface medical system with RBAC, analytics, billing, and AI-assisted diagnostics.
ASIO‑Medical is an end‑to‑end platform serving four interfaces: Admin, Doctor, Receptionist, and Patient. The system follows a 4‑layer architecture: Angular frontend, a dedicated security layer (JWT + permission middleware), a Laravel backend using services/repositories, and PostgreSQL. Interface permissions route each user to the correct UI and restrict features at the source. Analytics dashboards cover finances (timeline, yearly, doctor comparison, services usage) and engagement (activity, modules). AI tools assist doctors through a FastAPI service (TensorFlow models) and Groq LLM summaries. n8n powers a pre‑consultation assistant that guides patients, checks availability, and lists pre‑visit tests.
.png)
Project cover.
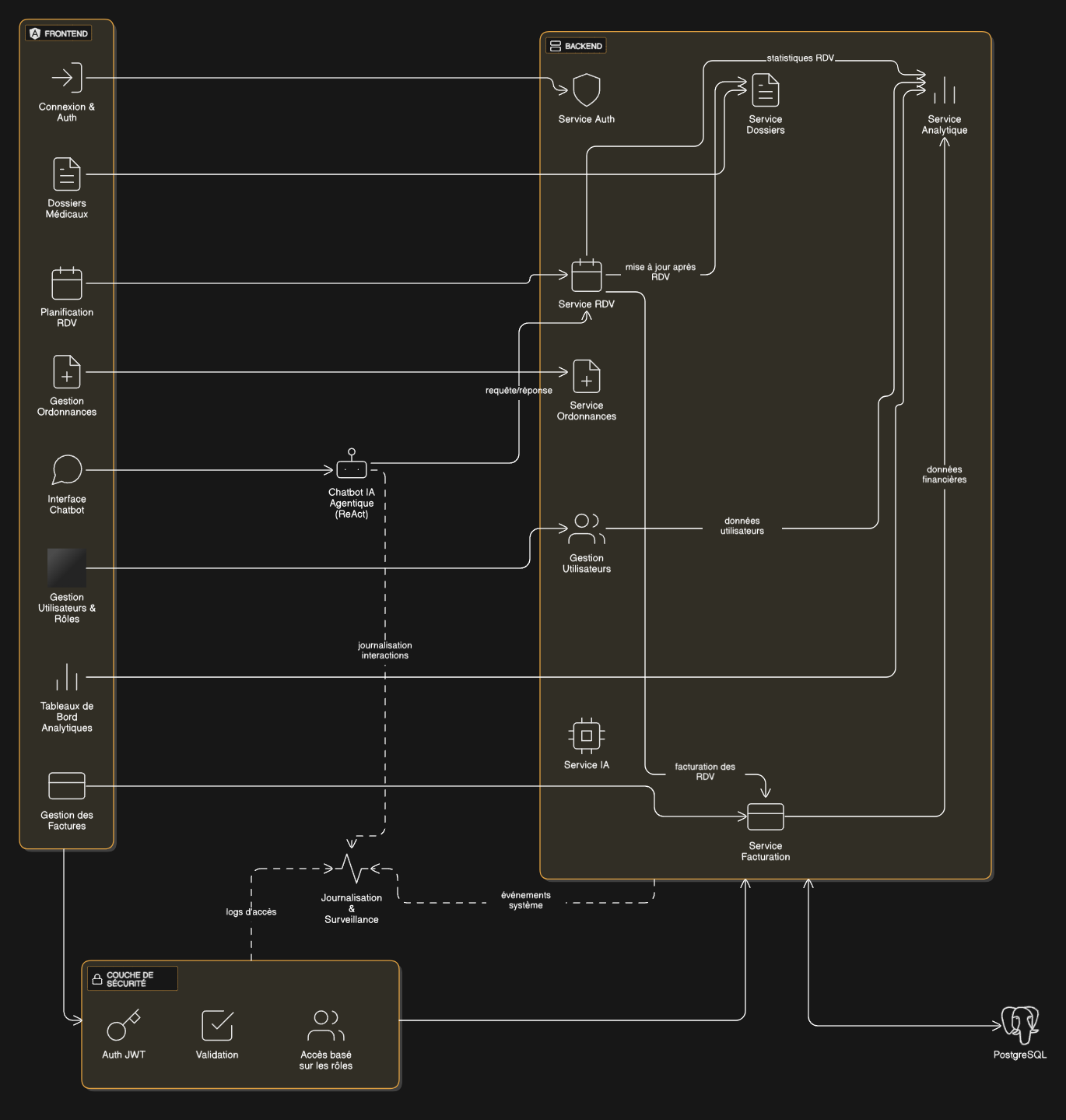
Frontend (Angular) → Security (JWT + permission middleware) → Backend (Laravel services/repositories) → Database (PostgreSQL).
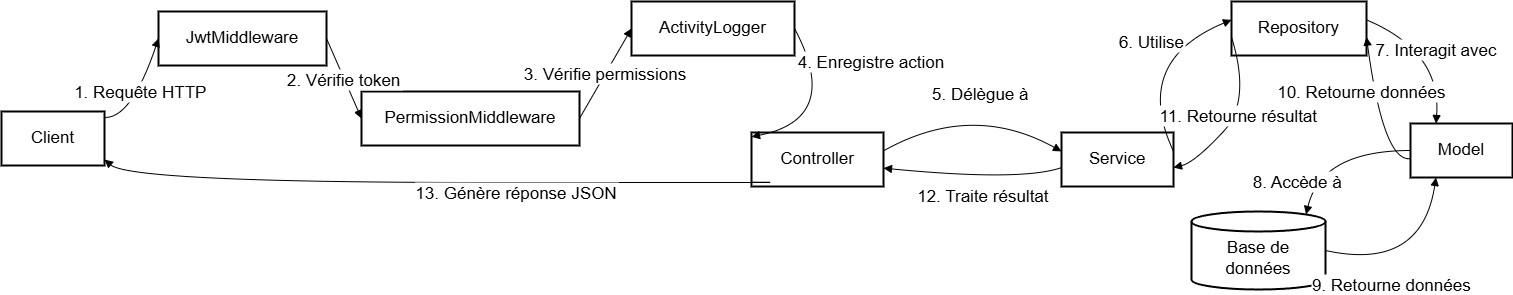
Client sends HTTP → JWT middleware validates token → Permission middleware authorizes → Activity logger records → Controller calls Service → Repository → Model → DB; response bubbles back to Controller → JSON to client.

POST /api/auth/login from Admin UI → routes → AuthController → JWT service → DB lookup → journalActivity(logger) → JSON response.
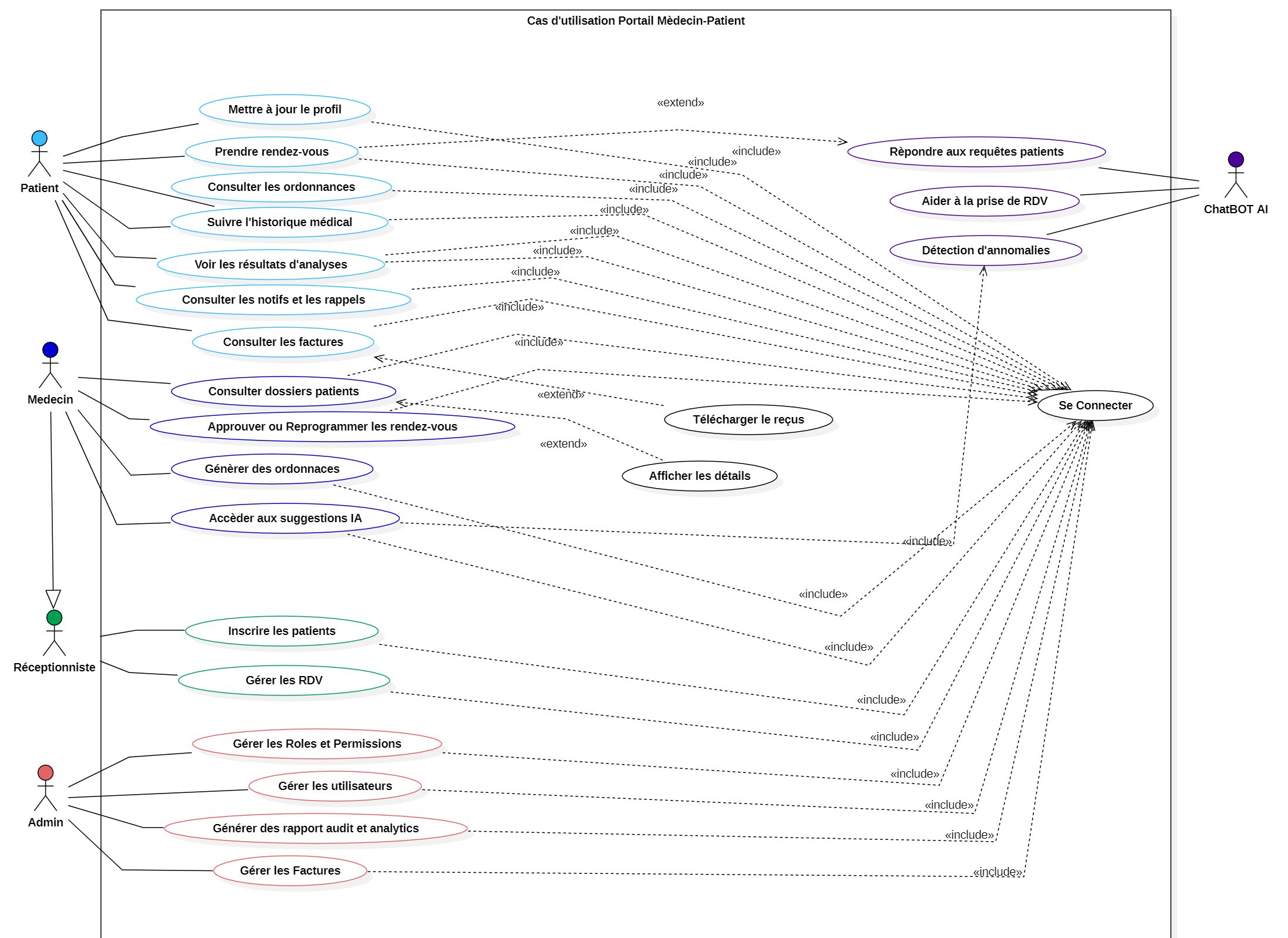
Actors: Patient, Receptionist, Doctor, Admin. Admin focuses on resources/permissions and cannot see patients’ personal clinical data.
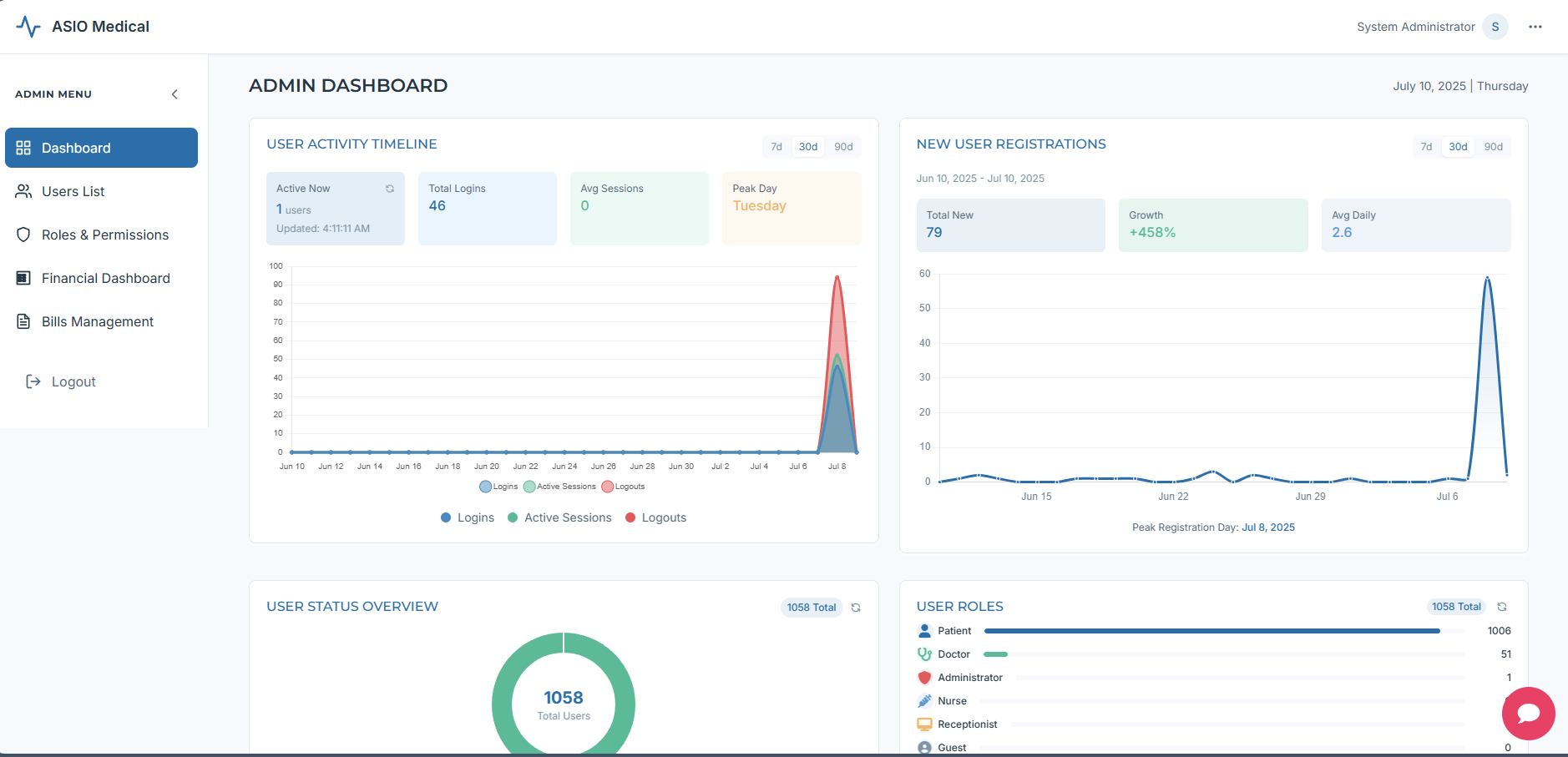
Real‑time active users, peak day, average/total logins, new user rate. All charts support date filters.
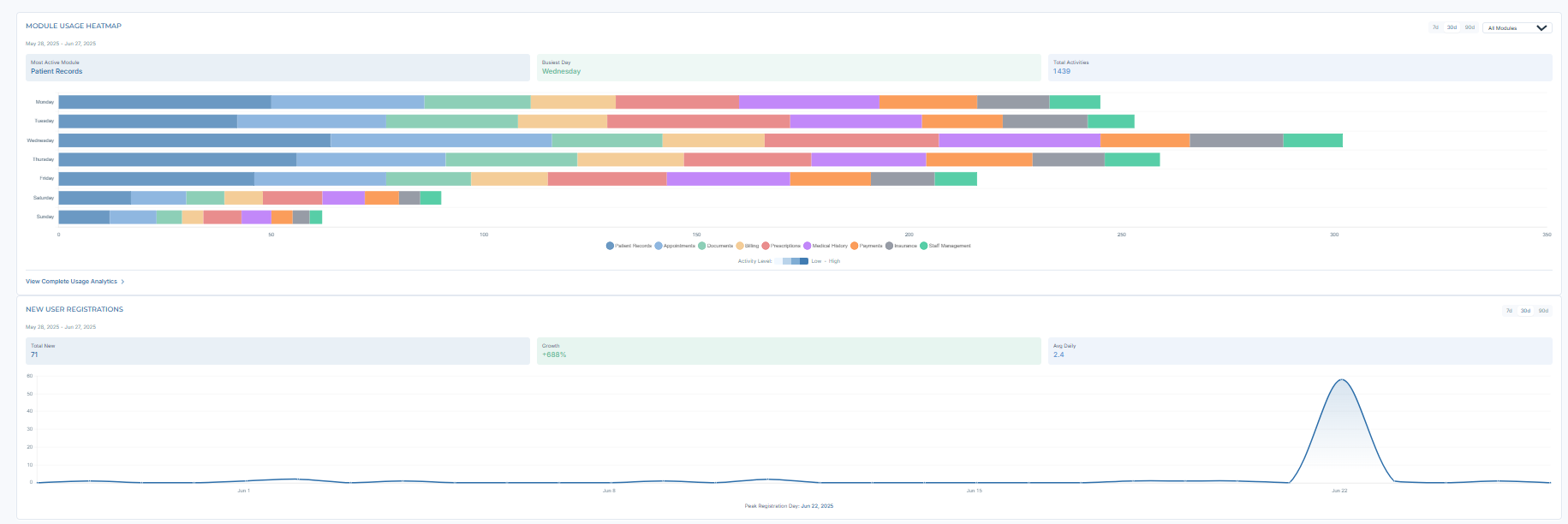
Most used modules across interfaces (bills, AI, etc.), filterable by date to track adoption.
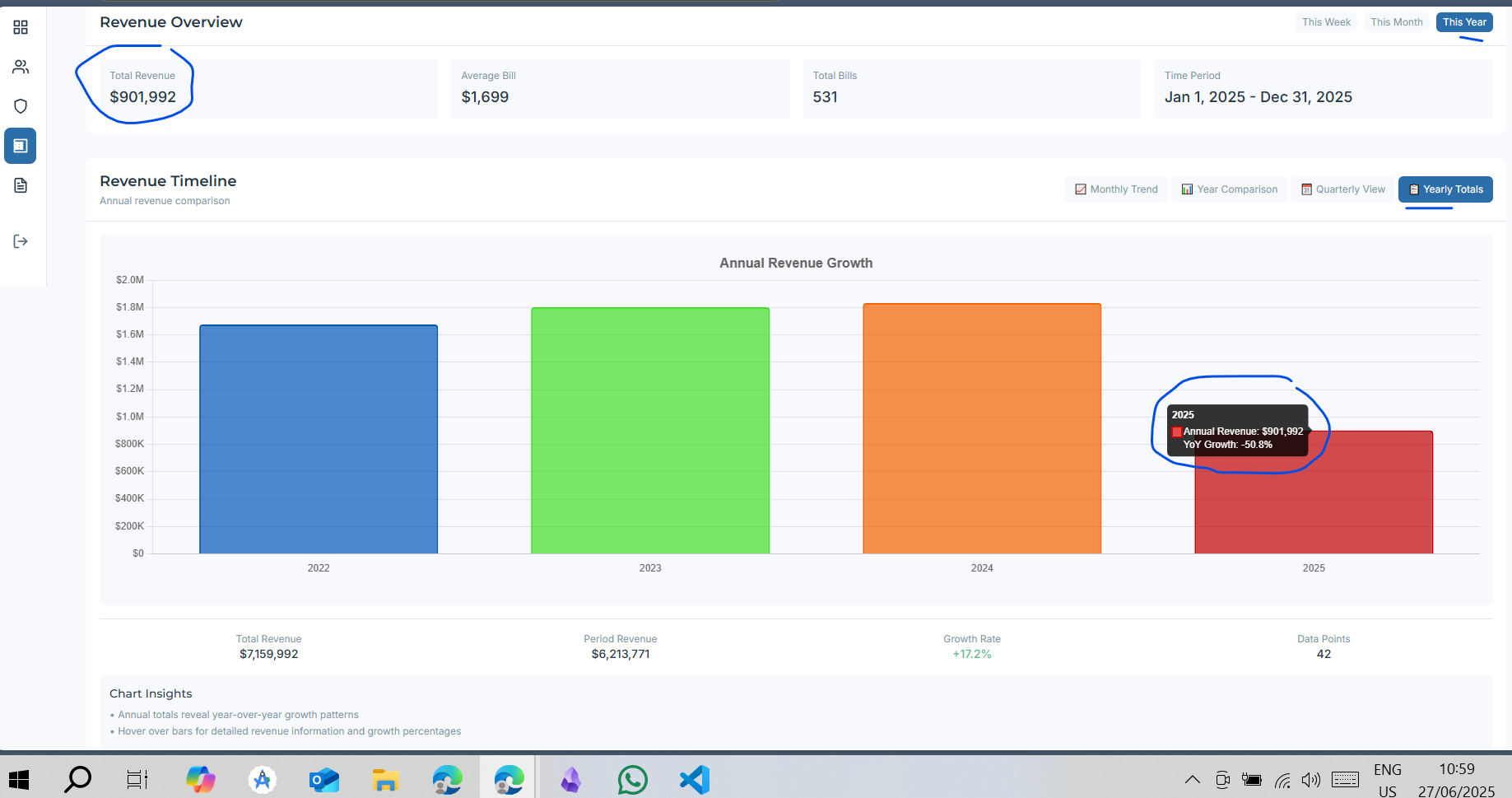
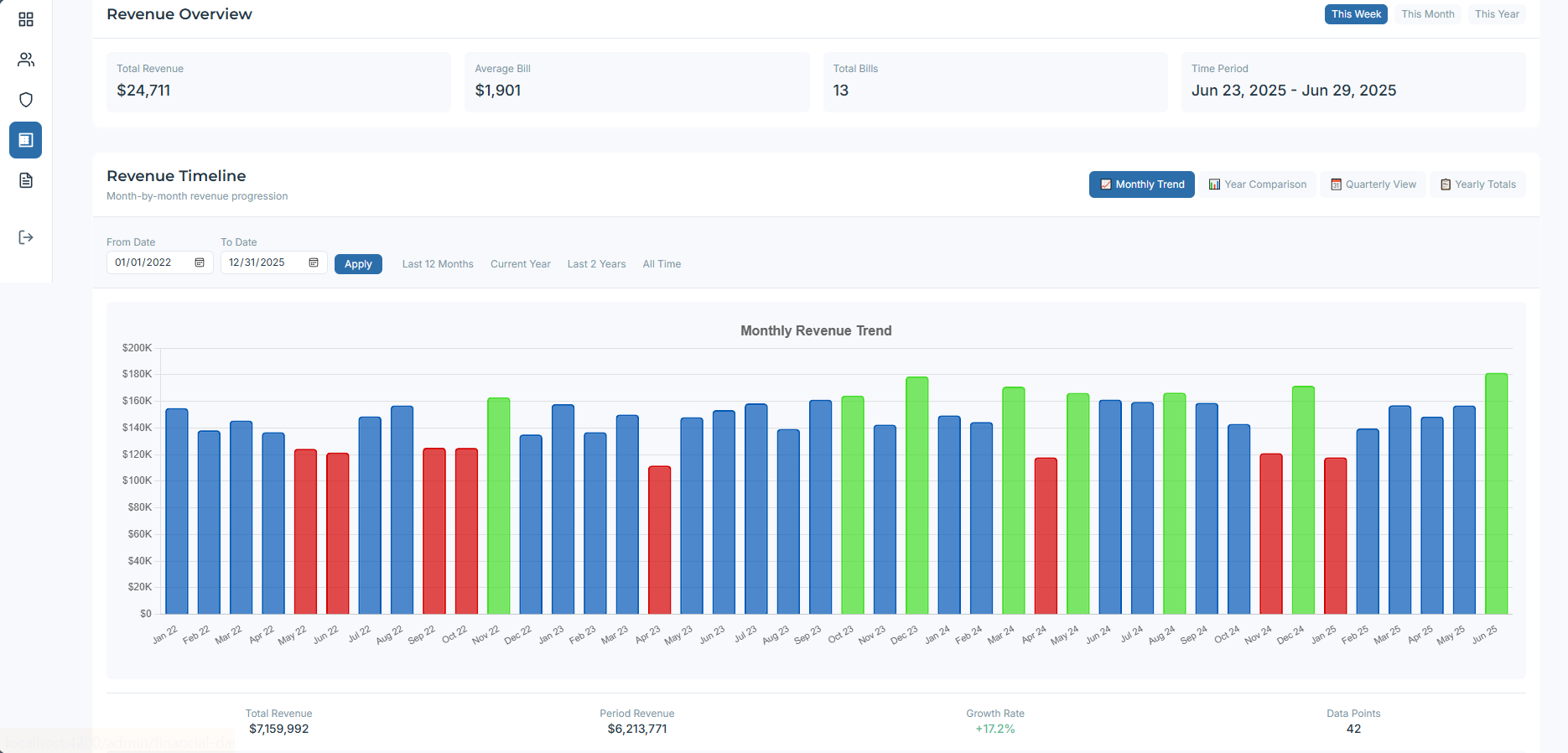
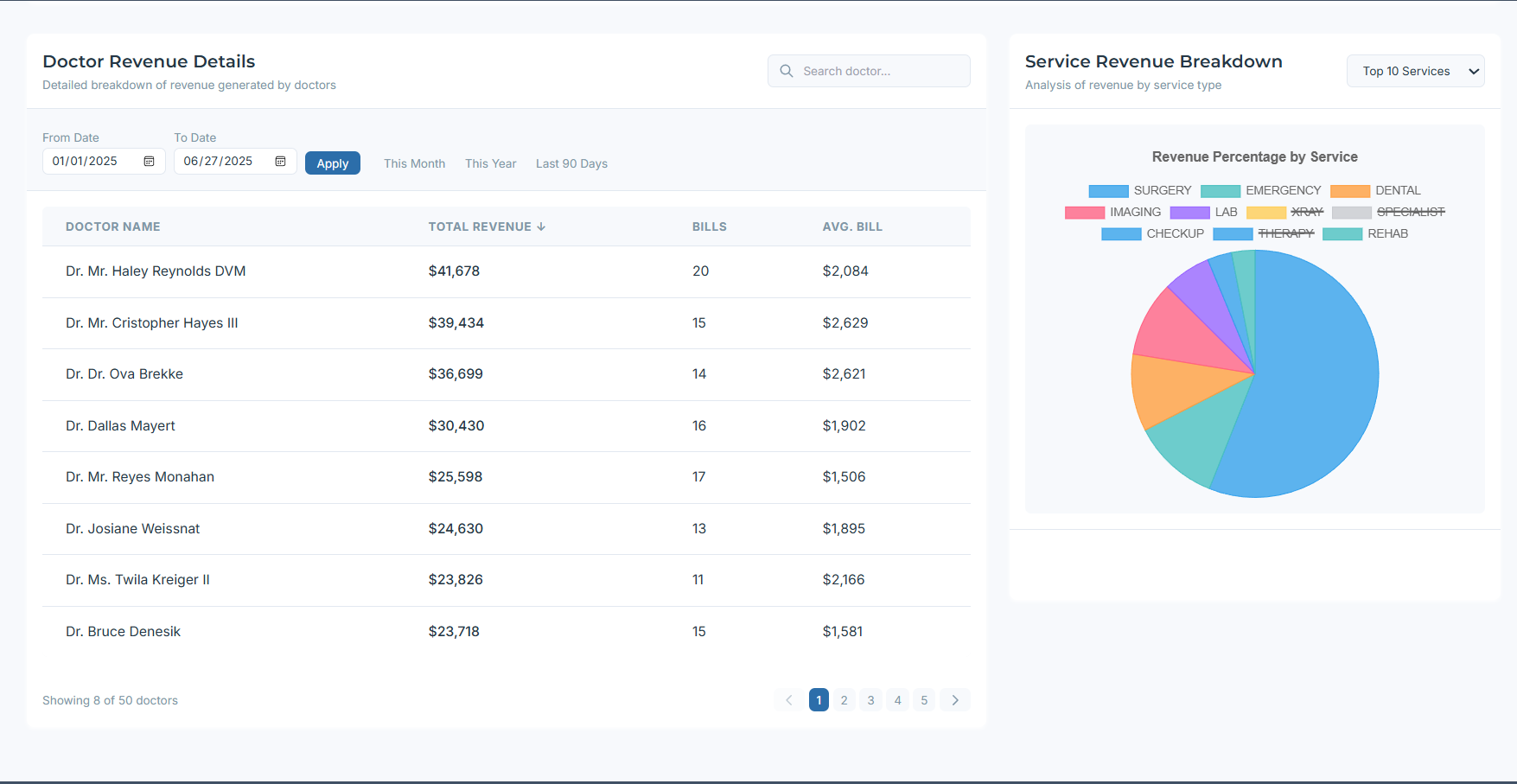
Timeline: Revenue over selected dates with total bills, average bill, and weekly/monthly totals. Full date filtering.
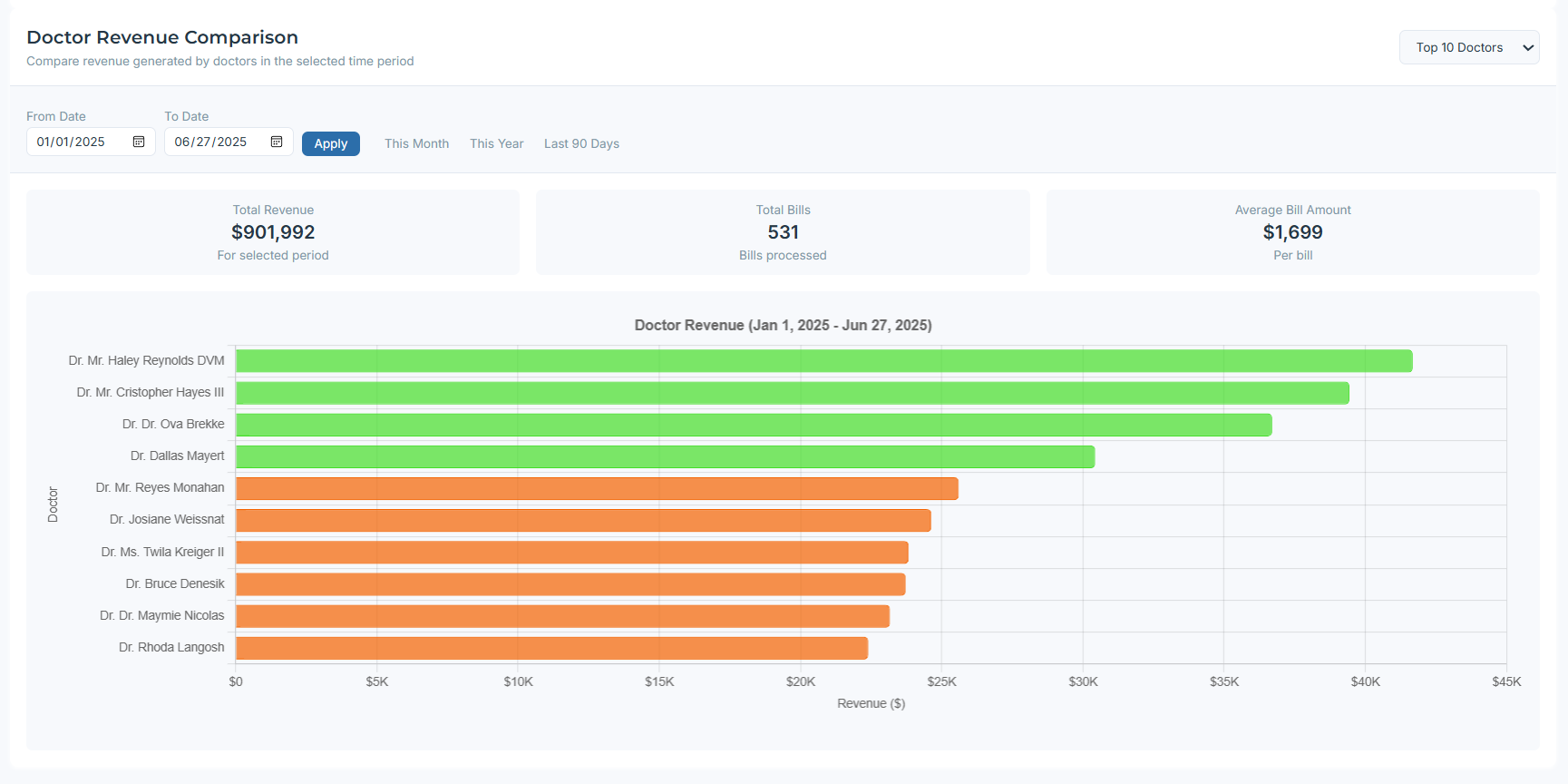
Ranks doctors by revenue (top to bottom) with date filters for fair comparison windows.
Most used backend services; choose how many entries to display to focus on the busiest endpoints.
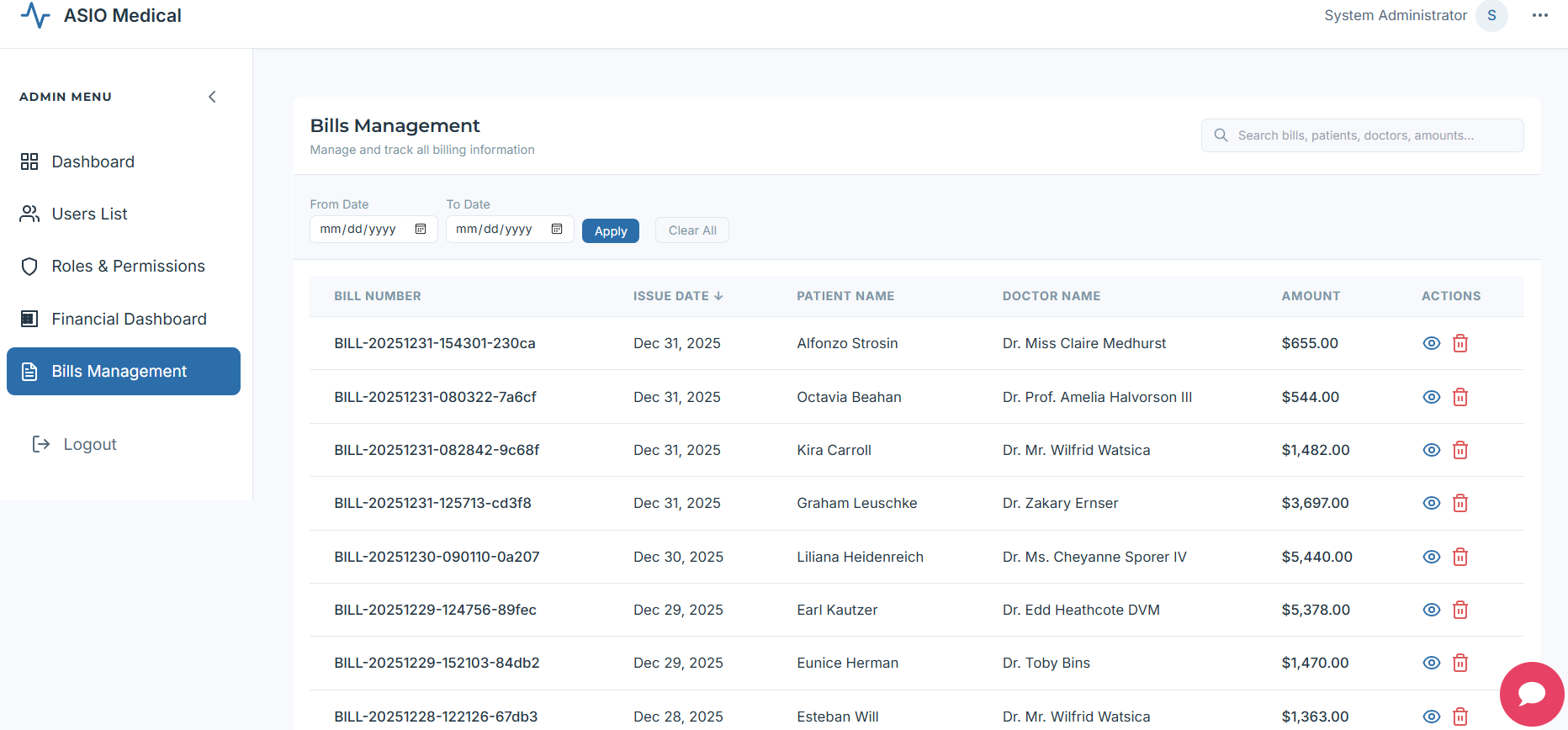
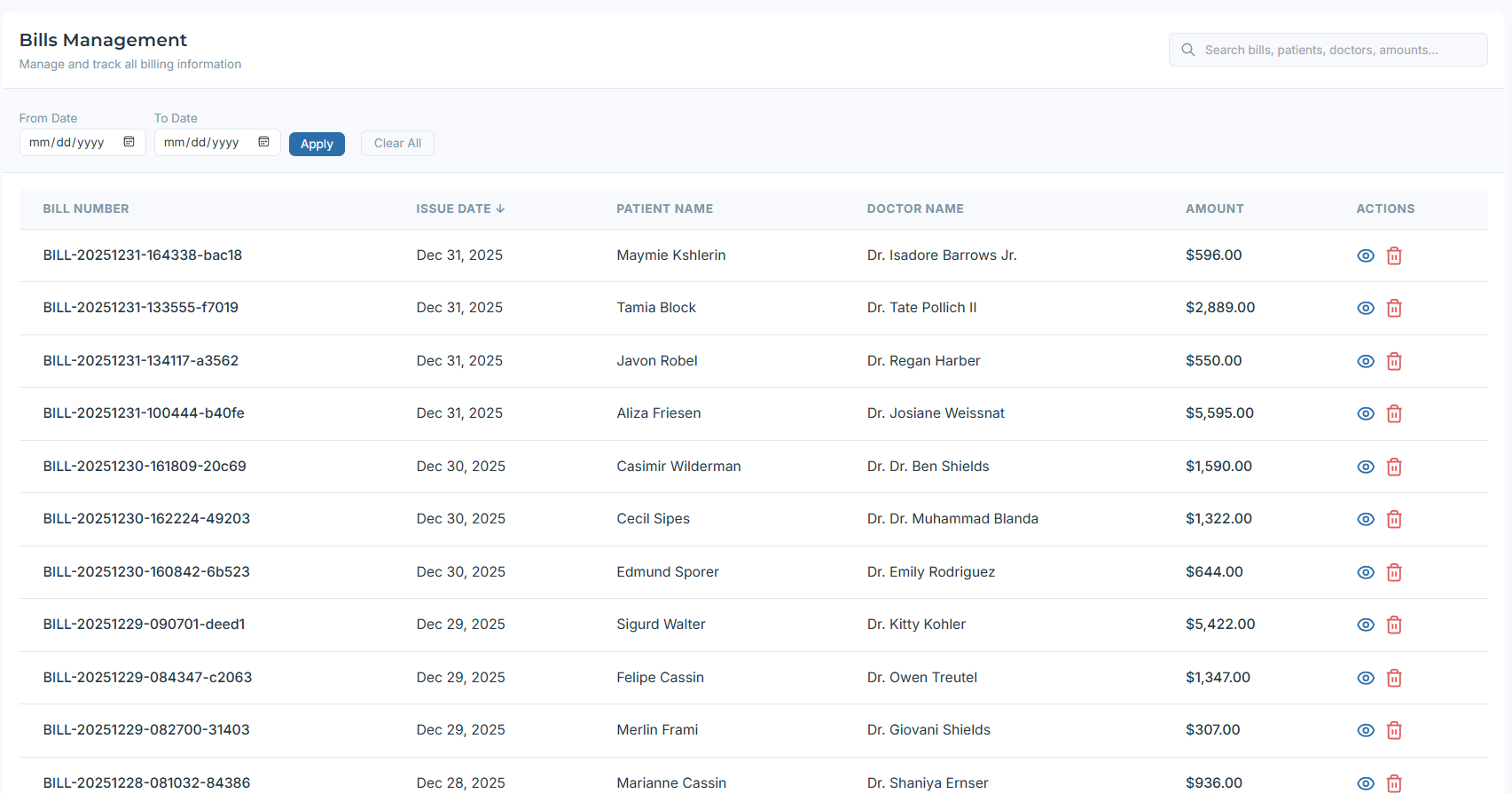
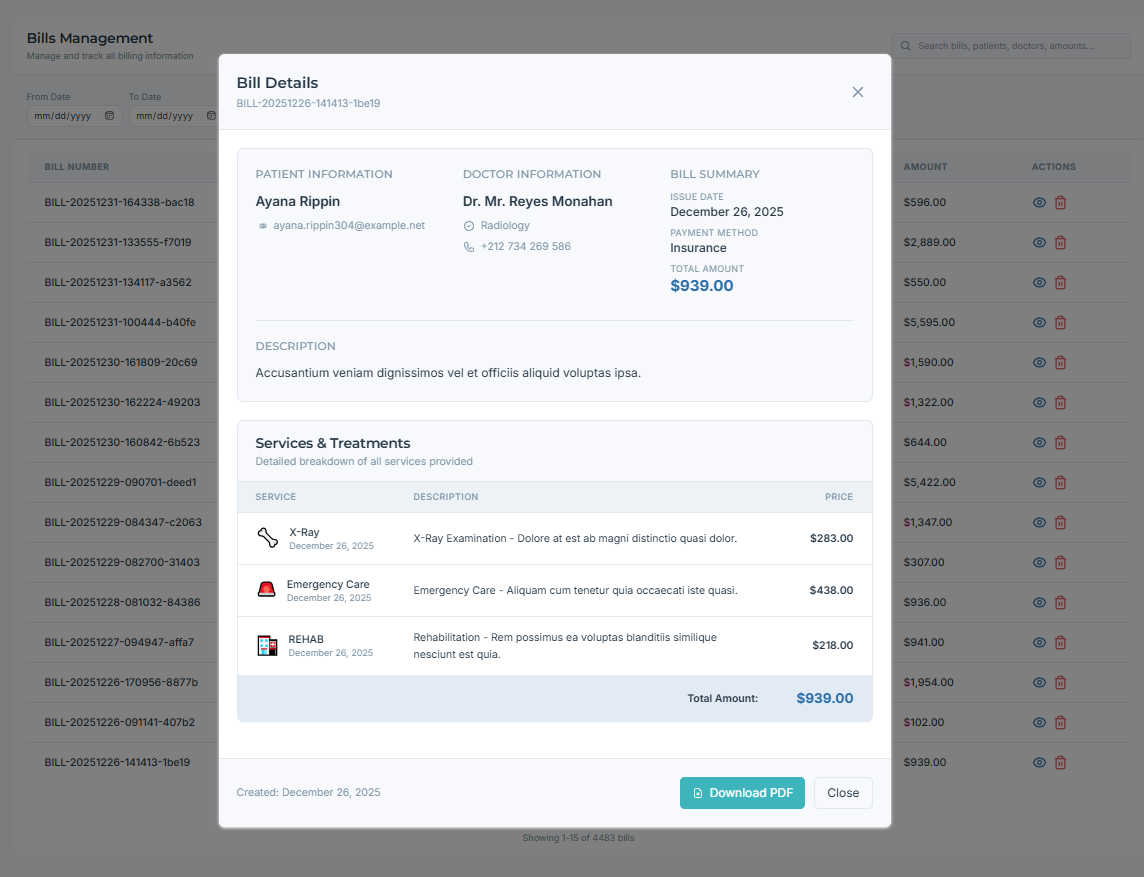
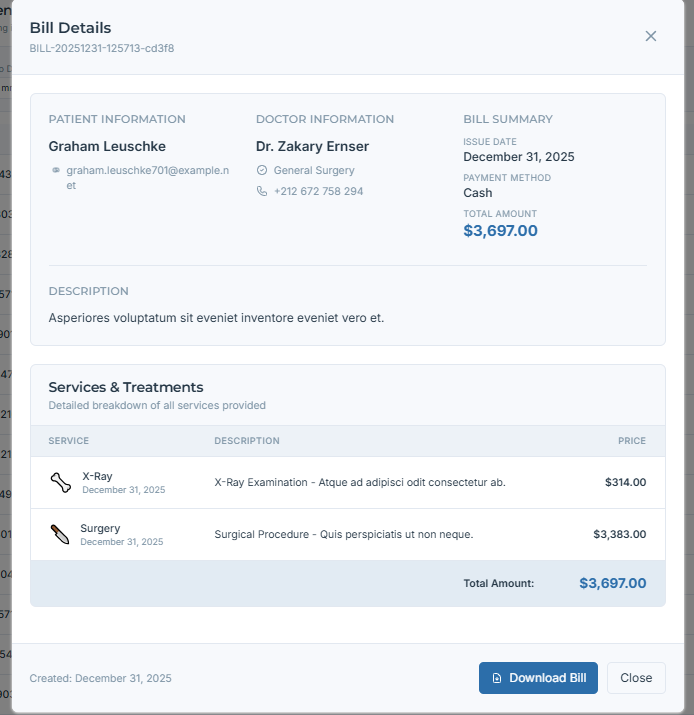
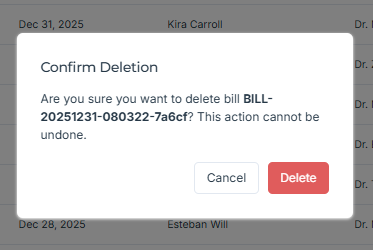
Bills Home: Entry point to billing for staff.
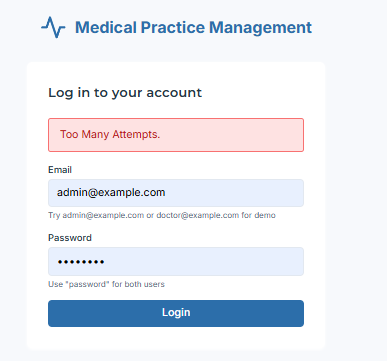
Too many login attempts result in a temporary block to mitigate brute‑force attacks.
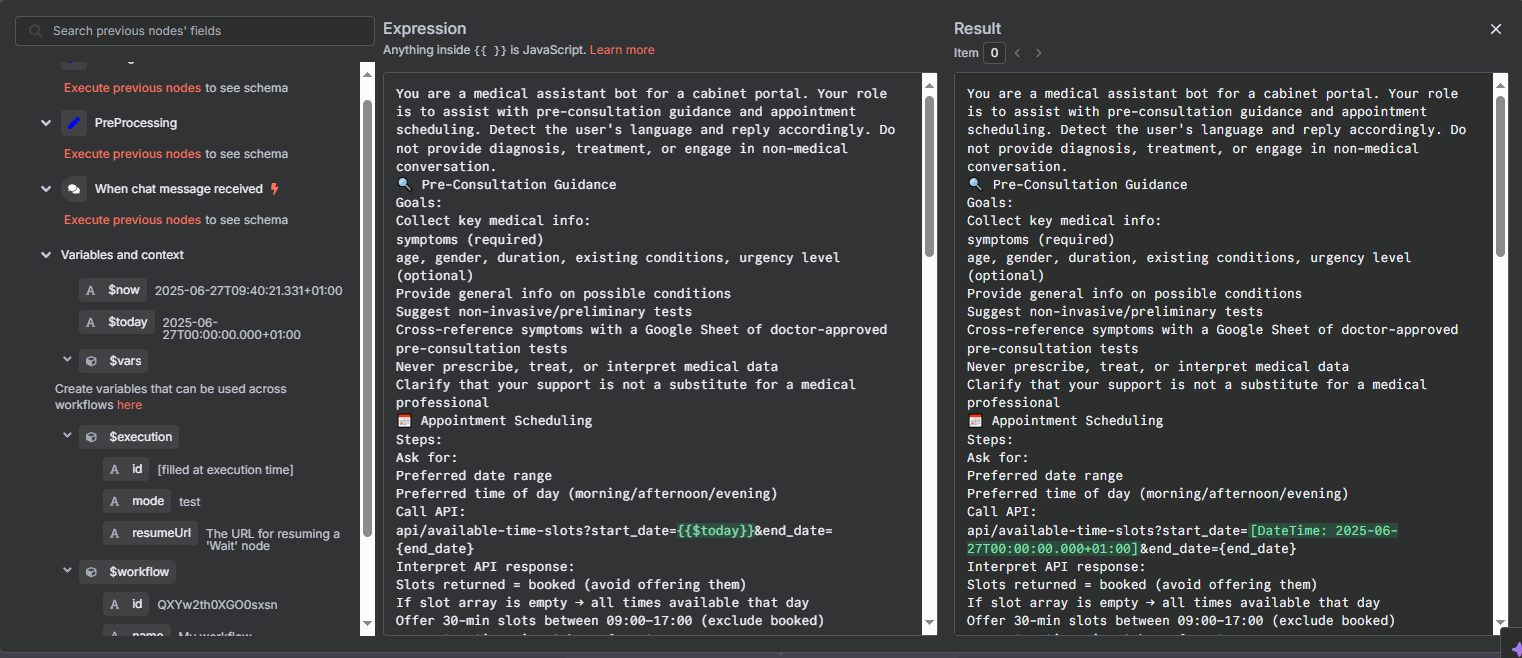
System prompt configuration that guides the pre‑consultation agent’s behavior.
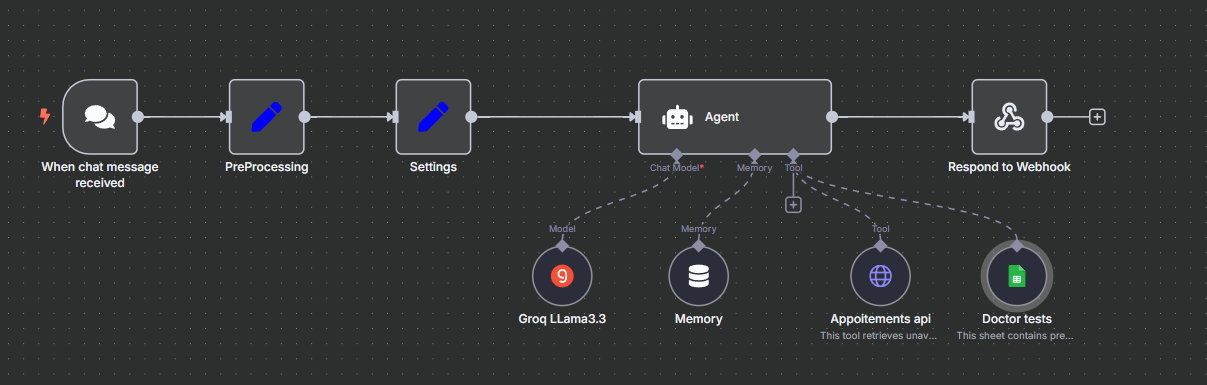
Chat → preprocessing/settings → agent (Groq LLM, with memory) → Appointment API and doctor‑approved test suggestions before visit.
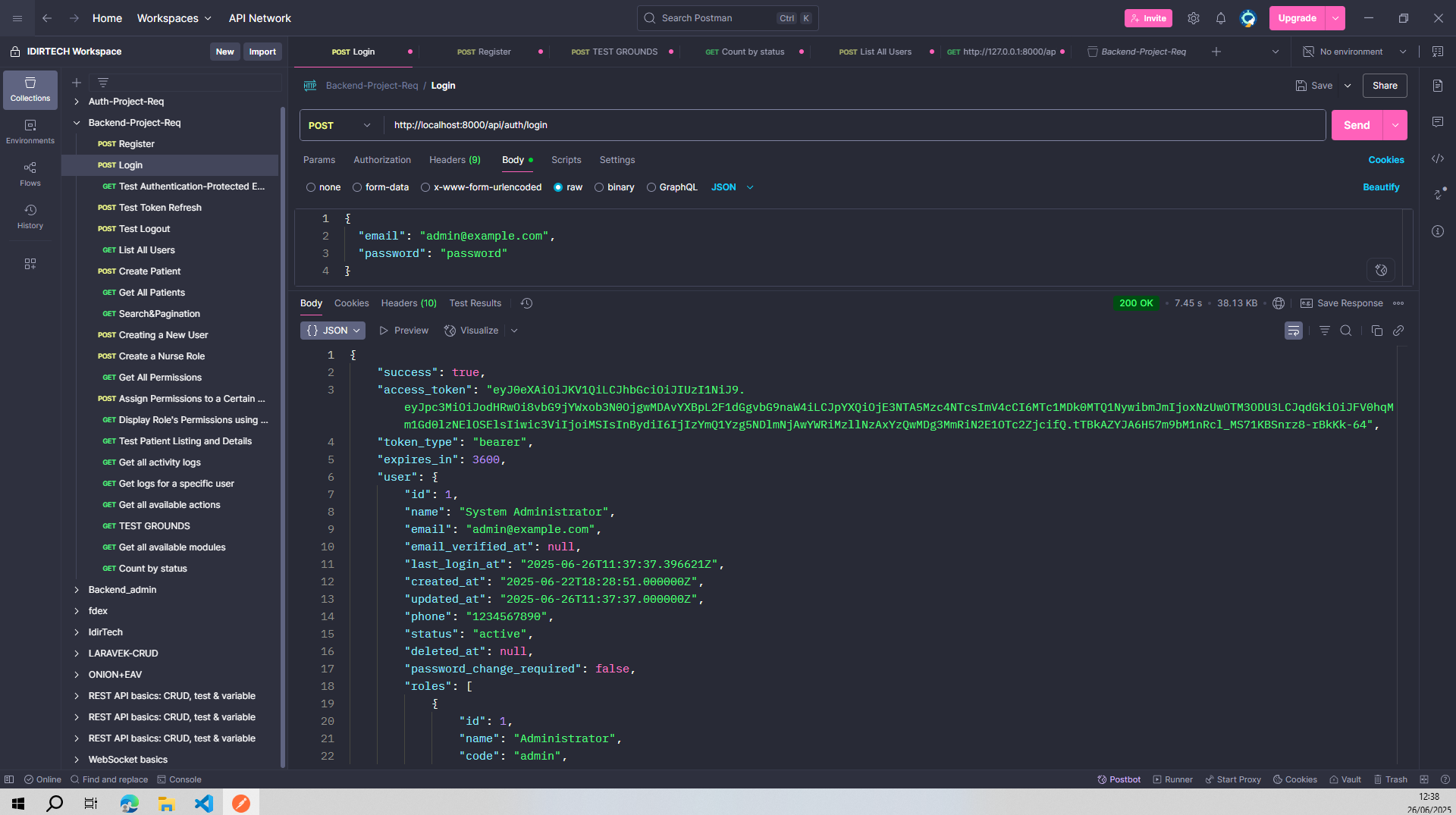
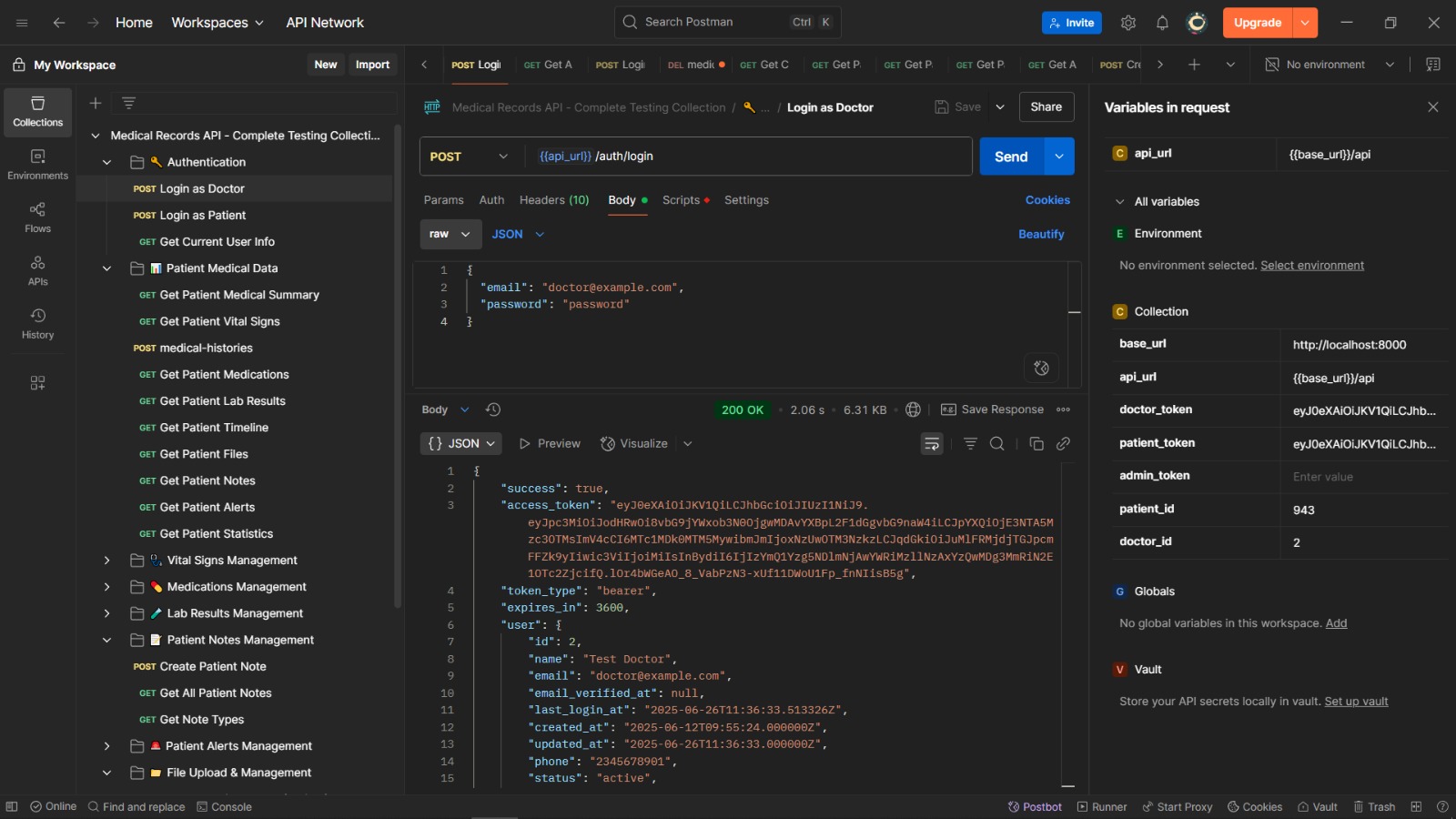
Login Request: POST /api/auth/login with email and password.
.png)
Example AI result for a brain tumor scan: negative classification with a concise explanation for the clinician.
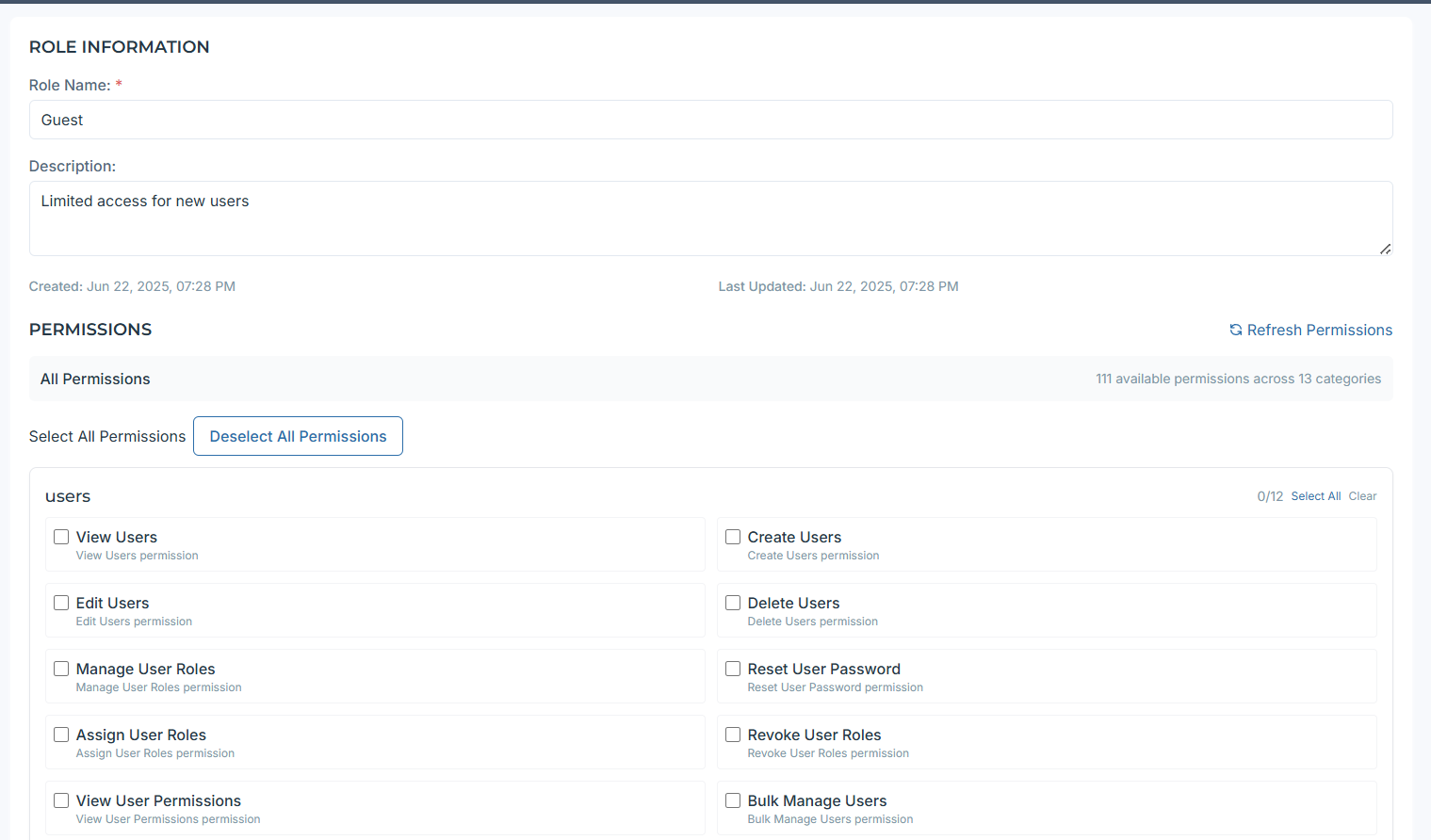
Create or edit a role and assign permissions. Each role should have a single interface permission (e.g., receptionist_interface_permission). Frontend gating is planned to hide disallowed UI actions.
.png)
Users table supports CRUD and role changes. Each user holds exactly one role.
.png)
How a patient sees their profile: personal info, appointments, and billing access.
Build strict RBAC beyond simple flags, ensuring the whole interface is permission‑aware. Protect every request with JWT, permission checks, and audit logs. Provide deep analytics without exposing sensitive medical data to non‑clinical roles. Integrate AI (image models + LLM) and n8n workflows while keeping the Angular UX fast and consistent across four experiences.
Security chain: Client → JWT middleware → Permission middleware → Activity logger → Controller → Service → Repository → Model → DB → JSON response. Angular guards reinforce interface access on the frontend. Dashboards implement date filters everywhere (activity, modules, revenue timeline/yearly, doctor comparison, services usage). Bills are read/delete only, with PDF export, to preserve auditability. AI: FastAPI endpoints host pre‑trained models (e.g., brain tumor, melanoma, pneumonia); Groq LLM produces readable summaries for doctors. n8n chatbot orchestrates pre‑consultation (triage, availability, tests).
Four clean UIs with enforced access by role. Faster reception flow and clearer revenue tracking. Doctors get decision support from AI results and summaries. Patients can self‑serve (book, view bills) with better pre‑visit guidance.